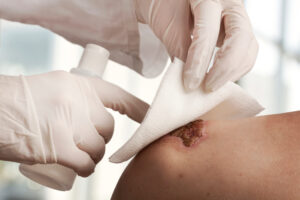
 Whenever you get a cut, scrape or any type of abrasion, the number one thing you want to prevent from happening is wound infection. When a wound becomes infected, it is due to bacteria entering through a break in the skin. Open wounds lack the protection typically offered by your epidermis making them highly susceptible to contamination.
Whenever you get a cut, scrape or any type of abrasion, the number one thing you want to prevent from happening is wound infection. When a wound becomes infected, it is due to bacteria entering through a break in the skin. Open wounds lack the protection typically offered by your epidermis making them highly susceptible to contamination.
Regularly cleaning your wound, keeping it properly covered and taking the proper steps to let your body rest and recover will help prevent a wound infection from developing. Wound infections commonly occur due to poor dressing techniques or exposure to unhygienic conditions. Staphylococcus aureus is the most common bacteria to cause wound infections.
How Do You Know If Your Wound Is Infected?
The most common signs of a wound infection include:
-The wound is warm, painful, swollen, and/or red.
-You see puss or blood oozing from the wound.
-The wound has developed an odd/foul odor.
-You notice your heart rate increase.
-You experience dizziness.
-Wound is not healing with time.
When a doctor looks at your wound they will ask you questions regarding your injury in order to determine the likelihood of wound infection. A number of tests can also be conducted such as a blood test, x-ray, CT or MRI scan, and a wound culture.
How To Treat Your Infected Wound
Once you know for certain that you have a wound infection there are treatment options available. Depending on underlying factors, the best course of action necessary to treat an infected wound will vary. Some of these factors include, how long the wound has been present, how long the infection has persisted, your overall health, as well as the wound’s severity and location.
The first step to treating any wound (infected or not) is to clean it thoroughly with soap and water in order to rinse away germs and reduce the risk for infection. Germ-killing products may also be used to intensify cleaning powers. Surgical cleaning may be used to remove any foreign objects lodged in the wound, including dirt, debris, objects, or dead tissue. In some cases, wet or dry dressings may be left inside of the wound in order to help the wound dry. The wound may also need to be drained to remove any infection.
Antibiotics (oral or topical) may be prescribed to help fight off infection.
NSAIDS may be prescribed to help reduce pain and/or fever. NSAIDS are known to cause kidney problems or stomach bleeding in some people. If you are currently on a blood thinner you should always ask your doctor before taking any other medications, including NSAIDS.
When Should You Visit Urgent Medical Center For Your Wound Infection?
If your wound becomes infected you will need to visit your doctor or local Urgent Medical Center. Urgent Care is highly recommended because you want to act as fast as possible with an infected wound.
Signs you should visit Urgent Medical Center for a wound infection include:
– The inside of your wound is a shade of dark or bright red.
– The pain, redness and swelling continue to increase instead of get better.
– Your wound remains swollen after 5 days.
– You notice new drainage developing.
– You notice a foul odor coming from your wound.
– You feel unsure and have any questions.
– You develop a fever or your glands begin to swell.
When is your wound infection serious enough to require a trip to the Emergency Room?
-Bandages continue to soak through with blood.
-Pain is very severe and getting worse.
-The skin surrounding your wound goes numb.
-Limbs located below the wound become immobilized.
-Your wound develops blisters.
-Your skin begins to peel or change colors.
(Learn More)
Risk Factors For Infected Wounds
There are certain risk factors that make you more susceptible to an infection developing in an open wound. These risk factors include:
-Any preexisting diseases or conditions such as diabetes, cancer, kidney, liver or lung conditions.
-If your wound has any foreign objects (such as glass or metal) stuck inside this can delay healing and lead to a greater chance of infection.
-If the wound has poor blood supply. Reasons blood supply may be crippled includes high blood pressure and blocked or narrowed blood vessels. The risks for poor blood supply increases if you smoke, have a preexisting heart condition, or blood vessel issues.
-If the wound is repeatedly injured the risk for infection increases.
-If you have a weakened immune system for any reason, including nutrition, certain medications you are taking, radiation treatment, etc.
Contact or visit Urgent Medical Center right away if you have an infected wound for the swift treatment you need to get on the road to recovery.